Breast cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in women, accounting for about 7% to 10% of all malignant tumors. Compared with most European and American countries, although the incidence of breast cancer in China is relatively low, it has increased in recent years, and some big cities have accounted for the first place in female malignant tumors. It often occurs in women aged 40 to 60 before and after menopause. More than 98% of breast cancer occurs in women, and only 1% to 2% in men.
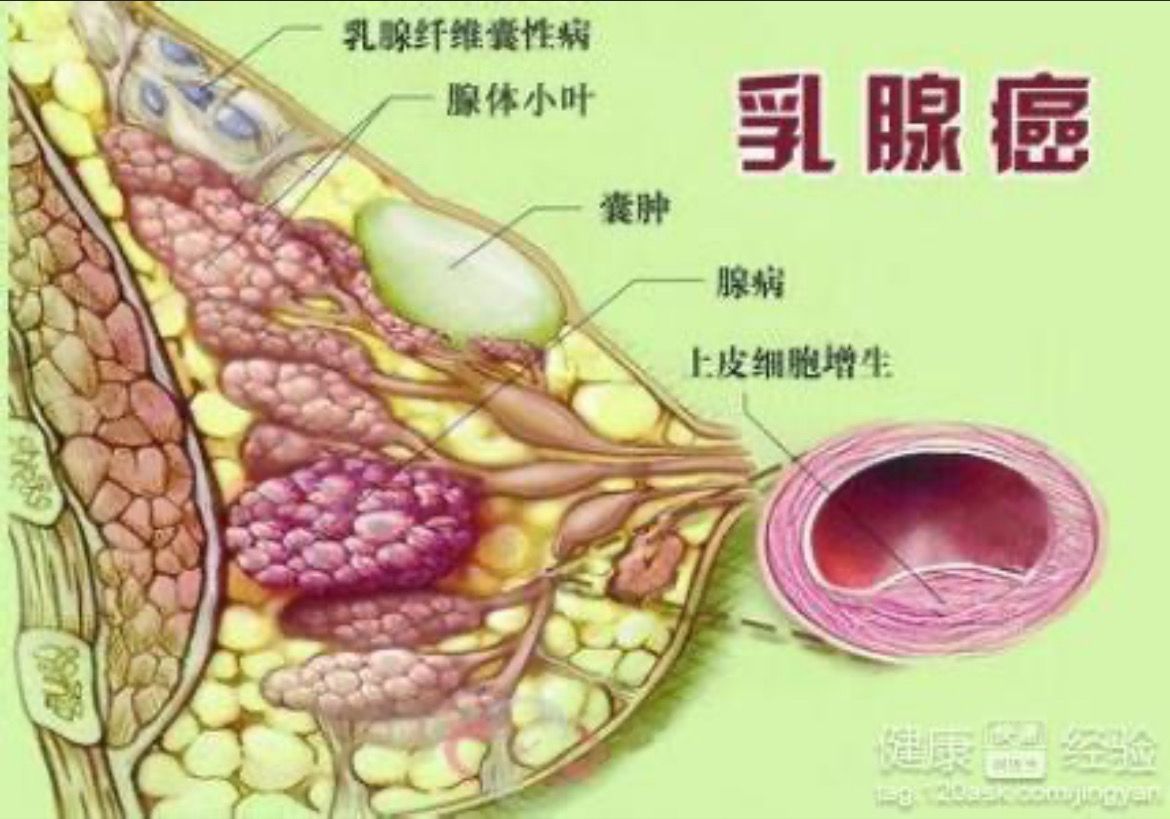
Breast cancer has the following manifestations:
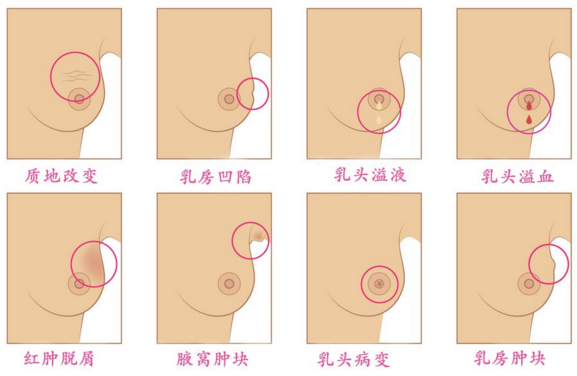
1. Clinical signs: 1. Early symptoms: Breast mass is the most common symptom, often located in the outer upper quadrant, mostly unilateral single, hard, unclear boundary, irregular shape, rough surface, poor activity, most of which are painless masses, a few of which have dull pain or tingling. 2. Medium-term symptoms: If the mass invades the ligament between the gland and the skin, it can pull the skin to form a depression, like a dimple; block lymphatic reflux, the skin is orange peel-like; infiltrate into the intradermal growth, it can form scattered skin hard nodules around the main lesion, called satellite nodules; When the lump invades the nipple and areola, it can be depressed by pulling the nipple, and in severe cases, it can be completely retracted behind the areola. 3. Symptoms in the middle and late stages: under non-physiological conditions, unilateral nipple discharge occurs, and the fluid is mostly serous, bloody or watery. Some patients will have cachexia, such as loss of appetite, anorexia, emaciation, fatigue, anemia, fever and other symptoms. 4. Late symptoms: local lymph node metastasis. The early manifestation is ipsilateral axillary lymph node enlargement, and with the development of the disease, it can metastasize to the supraclavicular and contralateral axilla, and some even have bone metastasis. 5. Other symptoms: Lung and pleural metastasis: Lung is the common metastatic site of breast cancer, mainly manifested as bilateral multiple nodules, patients may cough, expiratory dyspnoea, hemoptysis and other symptoms. Bone metastasis: It often metastasizes to vertebral bodies, ribs, pelvis and long bones, and can also occur in scapula, skull and other parts, mainly manifested as bone pain, hypercalcemia and so on. Liver metastasis: There are no special symptoms in the initial stage. When the mass is large or the scope is large, symptoms such as hepatomegaly, pain in the liver area and loss of appetite may occur.
2. Auxiliary examinations: (1) Tumor markers: CA15-3 and CEA are common, which provide reference for diagnosis and monitor prognosis and recurrence. (2) Other examinations: Mammography: The accuracy rate is 80% ~ 90%, which is of great significance in differentiating benign and malignant breast tumors and early diagnosis of breast cancer. Ultrasound: non-invasive, can be examined many times. The diagnostic accuracy of breast cancer was 80% ~ 90%. Cystic and solid masses can be differentiated. 3. Pathological biopsy: the gold standard for diagnosis. 4. Breast forceps target: It is of great significance to the small calcification of the breast. 5. Breast magnetic resonance imaging: It is mostly used to judge the staging of breast cancer, and it is of great significance for small lesions, multiple centers and multiple lesions.
3. Diagnosis: In clinical practice, the diagnosis can be confirmed through the summary of physical examination, symptoms and auxiliary examination information. For example, physical examination found breast mass, breast skin abnormalities and other typical symptoms, should be further examined by B-mode ultrasound, breast molybdenum target, magnetic resonance, and finally confirmed by pathological examination.
early detection, early diagnosis and early treatment: (1) Regular self-examination: pay attention to whether there is a breast mass, whether there is nipple discharge, and whether there is any change in breast shape. (2) Regular physical examination: Women over 30 years old should have a breast specialist examination at least once a year, and high-risk patients should have a breast specialist examination once every six months. To achieve early detection, early diagnosis and early treatment.
2. Multi-means comprehensive treatment: For patients who have been diagnosed with breast cancer, precise, individualized and comprehensive treatment based on molecular typing should be carried out according to the latest clinical guidelines for breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. At present, the main clinical treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, endocrine therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, traditional Chinese medicine and so on.